

Oral Surgery Procedures
Wisdom Teeth | Orthognathic Surgery | Facial Trauma | Dental Implants | Bone Grafting | Pre-Prosthetic Surgery | Platelet Rich Plasma | Impacted Canines | Oral Pathology | TMJ Disorders | Sleep Apnea
Wisdom Teeth
 By the age of 18, the average adult has 32 teeth; 16 teeth on the top and 16 teeth on the bottom. Each tooth in the mouth has a specific name and function. The teeth in the front of the mouth (incisors, canine, and bicuspid teeth) are ideal for grasping and biting food into smaller pieces. The back teeth (molar teeth) are used to grind food up into a consistency suitable for swallowing.
By the age of 18, the average adult has 32 teeth; 16 teeth on the top and 16 teeth on the bottom. Each tooth in the mouth has a specific name and function. The teeth in the front of the mouth (incisors, canine, and bicuspid teeth) are ideal for grasping and biting food into smaller pieces. The back teeth (molar teeth) are used to grind food up into a consistency suitable for swallowing.
The average mouth is made to hold only 28 teeth. It can be painful when 32 teeth try to fit in a mouth that holds only 28 teeth. These four other teeth are your third molars, also known as "wisdom teeth."
Why Should I Have My Wisdom Teeth Removed?
Wisdom teeth are the last teeth to erupt within the mouth. When they align properly and gum tissue is healthy, wisdom teeth do not have to be removed. Unfortunately, this does not generally happen. The extraction of wisdom teeth is necessary when they are prevented from properly erupting within the mouth. They may grow sideways, partially emerge from the gum, and even remain trapped beneath the gum and bone. Impacted teeth can take many positions in the bone as they attempt to find a pathway that will allow them to successfully erupt.
These poorly positioned impacted teeth can cause many problems. When they are partially erupted, the opening around the teeth allows bacteria to grow and will eventually cause an infection. The result: swelling, stiffness, pain, and illness. The pressure from the erupting wisdom teeth may move other teeth and disrupt the orthodontic or natural alignment of teeth. The most serious problem occurs when tumors or cysts form around the impacted wisdom teeth, resulting in the destruction of the jawbone and healthy teeth. Removal of the offending impacted teeth usually resolves these problems. Early removal is recommended to avoid such future problems and to decrease the surgical risk involved with the procedure.
Oral Examination
With an oral examination and x-rays of the mouth, Dr. Mills can evaluate the position of the wisdom teeth and predict if there are present or may be future problems. Studies have shown that early evaluation and treatment result in a superior outcome for the patient. Patients are generally first evaluated in the mid-teenage years by their dentist, orthodontist or by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
All outpatient surgery is performed under appropriate anesthesia to maximize patient comfort. Dr ( Mills) has the training, license and experience to provide various types of anesthesia for patients to select the best alternative.
Removal
In most cases, the removal of wisdom teeth is performed under local anesthesia, laughing gas (nitrous oxide/oxygen analgesia) or general anesthesia. These options, as well as the surgical risks (i.e., sensory nerve damage, sinus complications), will be discussed with you before the procedure is performed. Once the teeth are removed, the gum may be sutured. To help control bleeding, bite down on the gauze placed in your mouth. You will rest under our supervision in the office until you are ready to be taken home. Upon discharge, your postoperative kit will include postoperative instructions, a prescription for pain medication, antibiotics, and a follow-up appointment in one week for suture removal. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to call us at 925-443-4211.
Our services are provided in an environment of optimum safety that utilizes modern monitoring equipment and staff who are experienced in anesthesia techniques.
go to top >>Orthognathic Surgery
 Orthognathic surgery is needed when jaws don't meet correctly and/or teeth don't seem to fit with jaws. Teeth are straightened with orthodontics and corrective jaw surgery repositions a misaligned jaw. This not only improves facial appearance, but also ensures that teeth meet correctly and function properly.
Orthognathic surgery is needed when jaws don't meet correctly and/or teeth don't seem to fit with jaws. Teeth are straightened with orthodontics and corrective jaw surgery repositions a misaligned jaw. This not only improves facial appearance, but also ensures that teeth meet correctly and function properly.
Who Needs Orthognathic Surgery?
People who can benefit from orthognathic surgery include those with an improper bite or jaws that are positioned incorrectly. Jaw growth is a gradual process and in some instances, the upper and lower jaws may grow at different rates. The result can be a host of problems that can affect chewing function, speech, long-term oral health and appearance. Injury to the jaw and birth defects can also affect jaw alignment. Orthodontics alone can correct bite problems when only the teeth are involved. Orthognathic surgery may be required for the jaws when repositioning in necessary. Difficulty in the following areas should be evaluated:
Difficulty in chewing, biting or swallowing Speech problems Chronic jaw or TMJ pain Open bite Protruding jaw Breathing problems
Any of these symptoms can exist at birth, be acquired after birth as a result of hereditary or environmental influences, or as a result of trauma to the face. Before any treatment begins, a consultation will be held to perform a complete examination with x-rays. During the pre-treatment consultation process, feel free to ask any questions that you have regarding your treatment. When you are fully informed about the aspects of your care, you and your dental team can make the decision to proceed with treatment together. Technology & Orthognathic Surgery
Dr. Mills uses modern computer techniques and three-dimensional models to show you exactly how your surgery will be approached. Using comprehensive facial x-rays and computer video imaging, we can show you how your bite will be improved and even give you an idea of how you'll look after surgery. This helps you understand the surgical process and the extent of the treatment prescribed. Our goal is to help you understand the benefits of orthognathic surgery.
If you are a candidate for corrective jaw surgery, Dr. Mills will work closely with your dentist and orthodontist during your treatment. The actual surgery can move your teeth and jaws into a new position that results in a more attractive, functional, and healthy dental-facial relationship.
go to top >>Facial Trauma
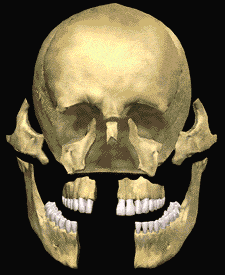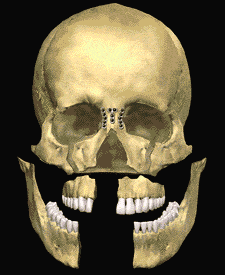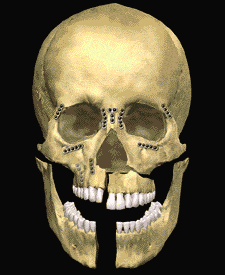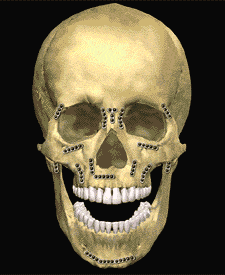 The dental specialist performs the proper treatment of facial injuries. These professionals must be well versed in emergency care, acute treatment and long-term reconstruction and rehabilitation – not just for physical reasons but emotional as well. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained, skilled and uniquely qualified to manage and treat facial trauma. Injuries to the face, by their very nature, impart a high degree of emotional, as well as physical trauma to patients. The science and art of treating these injuries requires special training involving a “hands on” experience and an understanding of how the treatment provided will influence the patient’s long term function and appearance.
The dental specialist performs the proper treatment of facial injuries. These professionals must be well versed in emergency care, acute treatment and long-term reconstruction and rehabilitation – not just for physical reasons but emotional as well. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained, skilled and uniquely qualified to manage and treat facial trauma. Injuries to the face, by their very nature, impart a high degree of emotional, as well as physical trauma to patients. The science and art of treating these injuries requires special training involving a “hands on” experience and an understanding of how the treatment provided will influence the patient’s long term function and appearance.
Dr. Mills meets and exceeds these modern standards. They are trained, skilled, and uniquely qualified to manage and treat facial trauma.
Facial lacerations Intra oral lacerations Avulsed (knocked out) teeth Fractured facial bones (cheek, nose or eye socket) Fractured jaws (upper and lower jaw)
The Nature Of Maxillofacial Trauma
There are a number of possible causes of facial trauma such as motor vehicle accidents, accidental falls, sports injuries, interpersonal violence, and work-related injuries. Types of facial injuries can range from injuries of teeth to extremely severe injuries of the skin and bones of the face. Typically, facial injuries are classified as either soft tissue injuries (skin and gums), bone injuries (fractures), or injuries to special regions (such as the eyes, facial nerves or the salivary glands).
Soft Tissue Injuries Of The Maxillofacial Region
When soft tissue injuries such as lacerations occur on the face, they are repaired by suturing. In addition to the obvious concern of providing a repair that yields the best cosmetic result possible, care is taken to inspect for and treat injuries to structures such as facial nerves, salivary glands, and salivary ducts (or outflow channels). Dr. Mills is a well-trained oral and maxillofacial surgeon and is proficient at diagnosing and treating all types of facial lacerations.
Bone Injuries Of The Maxillofacial Region
Fractures of the bones of the face are treated in a manner similar to the fractures in other parts of the body. The specific form of treatment is determined by various factors, which include the location of the fracture, the severity of the fracture, the age, and general health of the patient. When an arm or a leg is fractured, a cast is often applied to stabilize the bone to allow for proper healing. Since a cast cannot be placed on the face, other means have been developed to stabilize facial fractures.
One of these options involves wiring the jaws together for certain fractures of the upper and/or lower jaw. Certain other types of fractures of the jaw are best treated and stabilized by the surgical placement of small plates and screws at the involved site. This technique of treatment can often allow for healing and obviates the necessity of having the jaws wired together. This technique is called "rigid fixation" of a fracture. The relatively recent development and use of rigid fixation has profoundly improved the recovery period for many patients, allowing them to return to normal function more quickly.
The treatment of facial fractures should be accomplished in a thorough and predictable manner. More importantly, the patient's facial appearance should be minimally affected. An attempt at accessing the facial bones through the fewest incisions necessary is always made. At the same time, the incisions that become necessary, are designed to be small and, whenever possible, are placed so that the resultant scar is hidden.
Injuries To The Teeth & Surrounding Dental Structures
Isolated injuries to teeth are quite common and may require the expertise of various dental specialists. Oral surgeons usually are involved in treating fractures in the supporting bone or in replanting teeth that have been displaced or knocked out. These types of injuries are treated by one of a number of forms of splinting (stabilizing by wiring or bonding teeth together). If a tooth is knocked out, it should be placed in salt water or milk. The sooner the tooth is re-inserted into the dental socket, the better chance it will survive. Therefore, the patient should see a dentist or oral surgeon as soon as possible. Never attempt to wipe the tooth off, since remnants of the ligament that hold the tooth in the jaw are attached and are vital to the success of replanting the tooth. Other dental specialists may be called upon such as endodontists, who may be asked to perform root canal therapy, and/or restorative dentists who may need to repair or rebuild fractured teeth. In the event that injured teeth cannot be saved or repaired, dental implants are often now utilized as replacements for missing teeth.
The proper treatment of facial injuries is now the realm of specialists who are well versed in emergency care, acute treatment, long-term reconstruction, and rehabilitation of the patient.
go to top >>Bone Grafting Major & Minor Bone Grafting
 Over a period of time, the jawbone associated with missing teeth atrophies or is reabsorbed. This often leaves a condition in which there is poor quality and quantity of bone suitable for placement of dental implants. In these situations, most patients are not candidates for placement of dental implants.
Over a period of time, the jawbone associated with missing teeth atrophies or is reabsorbed. This often leaves a condition in which there is poor quality and quantity of bone suitable for placement of dental implants. In these situations, most patients are not candidates for placement of dental implants.
Today, we have the ability to grow bone where needed. This not only gives us the opportunity to place implants of proper length and width, it also gives us a chance to restore functionality and aesthetic appearance.
Major Bone Grafting
Bone grafting can repair implant sites with inadequate bone structure due to previous extractions, gum disease or injuries. The bone is either obtained from a tissue bank or your own bone is taken from the jaw, hip or tibia (below the knee). Sinus bone grafts are also performed to replace bone in the posterior upper jaw. In addition, special membranes may be utilized that dissolve under the gum and protect the bone graft and encourage bone regeneration. This is called guided bone regeneration or guided tissue regeneration.
Major bone grafts are typically performed to repair defects of the jaws. These defects may arise as a result of traumatic injuries, tumor surgery, or congenital defects. Large defects are repaired using the patient’s own bone. This bone is harvested from a number of different sites depending on the size of the defect. The skull (cranium), hip (iliac crest), and lateral knee (tibia), are common donor sites. These procedures are routinely performed in an operating room and require a hospital stay.
Sinus Lift Procedure
The maxillary sinuses are behind your cheeks and on top of the upper teeth. Sinuses are like empty rooms that have nothing in them. Some of the roots of the natural upper teeth extend up into the maxillary sinuses. When these upper teeth are removed, there is often just a thin wall of bone separating the maxillary sinus and the mouth. Dental implants need bone to hold them in place. When the sinus wall is very thin, it is impossible to place dental implants in this bone.
There is a solution and it’s called a sinus graft or sinus lift graft. The dental implant surgeon enters the sinus from where the upper teeth used to be. The sinus membrane is then lifted upward and donor bone is inserted into the floor of the sinus. Keep in mind that the floor of the sinus is the roof of the upper jaw. After several months of healing, the bone becomes part of the patient’s jaw and dental implants can be inserted and stabilized in this new sinus bone.
The sinus graft makes it possible for many patients to have dental implants when years ago there was no other option other than wearing loose dentures.
If enough bone between the upper jaw ridge and the bottom of the sinus is available to stabilize the implant well, sinus augmentations and implant placement can sometimes be performed as a single procedure. If not enough bone is available, the sinus augmentation will have to be performed first, then the graft will have to mature for several months, depending upon the type of graft material used. Once the graft has matured, the implants can be placed.
Ridge Expansion
In severe cases, the ridge has been reabsorbed and a bone graft is placed to increase ridge height and/or width. This is a technique used to restore the lost bone dimension when the jaw ridge gets too thin to place conventional implants. In this procedure, the bony ridge of the jaw is literally expanded by mechanical means. Bone graft material can be placed and matured for a few months before placing the implant.
Nerve Repositioning
The inferior alveolar nerve, which gives feeling to the lower lip and chin, may need to be moved in order to make room for placement of dental implants in the lower jaw. This procedure is limited to the lower jaw and indicated when teeth are missing in the area of the two back molars and/or and second premolar, with the above-mentioned secondary condition. Since this procedure is considered a very aggressive approach (there is almost always some postoperative numbness of the lower lip and jaw area, which dissipates only very slowly, if ever), usually other, less aggressive options are considered first (placement of blade implants, etc.).
Typically, an outer section of the cheek side of the lower jawbone is removed in order to expose the nerve and vessel canal. Then we isolate the nerve and vessel bundle in that area and slightly pull it out to the side. At the same time, we will place the implants. Then the bundle is released and placed back over the implants. The surgical access is refilled with bone graft material of the surgeon’s choice and the area is closed.
These procedures may be performed separately or together, depending upon the individual's condition. As stated earlier, there are several areas of the body that are suitable for attaining bone grafts. In the maxillofacial region, bone grafts can be taken from inside the mouth, in the area of the chin or third molar region, or in the upper jaw behind the last tooth. In more extensive situations, a greater quantity of bone can be attained from the hip or the outer aspect of the tibia at the knee. When we use the patient’s own bone for repairs, we generally get the best results.
In many cases, we can use allograft material to implement bone grafting for dental implants. This bone is prepared from cadavers and used to promote the patients own bone to grow into the repair site. It is quite effective and very safe. Synthetic materials can also be used to stimulate bone formation. We even use factors from your own blood to accelerate and promote bone formation in graft areas.
These surgeries are performed in the out-office surgical suite under IV sedation or general anesthesia. After discharge, bed rest is recommended for one day and limited physical activity for one week.
go to top >>Pre-Prosthetic Surgery
The preparation of your mouth before the placement of a prosthesis is referred to as pre-prosthetic surgery.
Some patients require minor oral surgical procedures before receiving a partial or complete denture, in order to ensure the maximum level of comfort. A denture sits on the bone ridge, so it is very important that the bone is the proper shape and size. If a tooth needs to be extracted, the underlying bone might be left sharp and uneven. For the best fit of a denture, the bone might need to be smoothed out or reshaped. Occasionally, excess bone would need to be removed prior to denture insertion.
One or more of the following procedures might need to be performed in order to prepare your mouth for a denture:
- Bone smoothing and reshaping
- Removal of excess bone
- Bone ridge reduction
- Removal of excess gum tissue
- Exposure of impacted teeth
We will review your particular needs with you during your appointment.
go to top >>Platelet Rich Plasma
Platelet rich plasma (PRP) is exactly what the name suggests. The substance is a by-product of blood (plasma) that is rich in platelets. Until now, its use has been confined to the hospital setting. This was due mainly to the cost of separating the platelets from the blood (thousands) and the large amount of blood needed (one unit) to produce a suitable quantity of platelets. New technology permits the doctor to harvest and produce a sufficient quantity of platelets from only 55 cc of blood drawn from the patient while they are having outpatient surgery.
Why All The Excitement About PRP?
PRP permits the body to take advantage of the normal healing pathways at a greatly accelerated rate. During the healing process, the body rushes many cells and cell-types to the wound in order to initiate the healing process. One of those cell types is platelets. Platelets perform many functions, including formation of a blood clot and release of growth factors (GF) into the wound. These GF (platelet derived growth factors PGDF, transforming growth factor beta TGF, and insulin-like growth factor ILGF) function to assist the body in repairing itself by stimulating stem cells to regenerate new tissue. The more growth factors released sequestered into the wound, the more stem cells stimulated to produce new host tissue. Thus, one can easily see that PRP permits the body to heal faster and more efficiently.
A subfamily of TGF, is bone morphogenic protein (BMP). BMP has been shown to induce the formation of new bone in research studies in animals and humans. This is of great significance to the surgeon who places dental implants. By adding PRP, and thus BMP, to the implant site with bone substitute particles, the implant surgeon can now grow bone more predictably and faster than ever before.
PRP Has Many Clinical Applications
Bone grafting for dental implants. This includes onlay and inlay grafts, sinus lift procedures, ridge augmentation procedures, and closure of cleft, lip, and palate defects. Repair of bone defects creating by removal of teeth or small cysts. Repair of fistulas between the sinus cavity and mouth.
PRP Also Has Many Advantages
Safety: PRP is a by-product of the patient’s own blood, therefore, disease transmission is not an issue.
Convenience: PRP can be generated in the doctor’s office while the patient is undergoing an outpatient surgical procedure, such as placement of dental implants.
Faster healing: The supersaturation of the wound with PRP, and thus growth factors, produces an increase of tissue synthesis and thus faster tissue regeneration.
Cost effectiveness: Since PRP harvesting is done with only 55 cc of blood in the doctor’s office, the patient need not incur the expense of the harvesting procedure in hospital or at the blood bank.
Ease of use: PRP is easy to handle and actually improves the ease of application of bone substitute materials and bone grafting products by making them more gel-like.
Frequently Asked Questions About PRP
Is PRP safe? Yes. During the outpatient surgical procedure a small amount of your own blood is drawn out via the IV. This blood is then placed in the PRP centrifuge machine and spun down. In less than 15 minutes, the PRP is formed and ready to use.
Should PRP be used in all bone-grafting cases? Not always. In some cases, there is no need for PRP. However, in the majority of cases, application of PRP to the graft will increase the final amount of bone present in addition to making the wound heal faster and more efficiently.
Will my insurance cover the costs? Unfortunately not.
Can PRP be used alone to stimulate bone formation? No. PRP must be mixed with either the patient’s own bone, a bone substitute material such as demineralized freeze-dried bone, or a synthetic bone product, such as BIO-OSS.
Are there any contraindications to PRP? Very few. Obviously, patients with bleeding disorders or hematologic diseases do not qualify for this in-office procedure. Check with your surgeon and/or primary care physician to determine if PRP is right for you.
go to top >>Impacted Canines
An impacted tooth simply means that it is “stuck” and cannot erupt into function. Patients frequently develop problems with impacted third molar (wisdom) teeth. These teeth get “stuck” in the back of the jaw and can develop painful infections among a host of other problems (see Impacted Wisdom Teeth under Procedures). Since there is rarely a functional need for wisdom teeth, they are usually extracted if they develop problems. The maxillary cuspid (upper eyetooth) is the second most common tooth to become impacted. The cuspid tooth is a critical tooth in the dental arch and plays an important role in your “bite”. The cuspid teeth are very strong biting teeth and have the longest roots of any human teeth. They are designed to be the first teeth that touch when your jaws close together so they guide the rest of the teeth into the proper bite.
Normally, the maxillary cuspid teeth are the last of the “front” teeth to erupt into place. They usually come into place around age 13 and cause any space left between the upper front teeth to close tighter together. If a cuspid tooth gets impacted, every effort is made to get it to erupt into its proper position in the dental arch. The techniques involved to aid eruption can be applied to any impacted tooth in the upper or lower jaw, but most commonly they are applied to the maxillary cuspid (upper eye) teeth. Sixty percent of these impacted eyeteeth are located on the palatal (roof of the mouth) side of the dental arch. The remaining impacted eye teeth are found in the middle of the supporting bone but stuck in an elevated position above the roots of the adjacent teeth or out to the facial side of the dental arch.
Early Recognition Of Impacted Eyeteeth Is The Key To Successful Treatment
The older the patient, the more likely an impacted eyetooth will not erupt by nature’s forces alone even if the space is available for the tooth to fit in the dental arch. The American Association of Orthodontists recommends that a panorex screening x-ray, along with a dental examination, be performed on all dental patients at around the age of seven years to count the teeth and determine if there are problems with eruption of the adult teeth. It is important to determine whether all the adult teeth are present or are some adult teeth missing. Are there extra teeth present or unusual growths that are blocking the eruption of the eyetooth? Is there extreme crowding or too little space available causing an eruption problem with the eyetooth? This exam is usually performed by your general dentist or hygienist who will refer you to an orthodontist if a problem is identified. Treating such a problem may involve an orthodontist placing braces to open spaces to allow for proper eruption of the adult teeth. Treatment may also require referral to an oral surgeon for extraction of over-retained baby teeth and/or selected adult teeth that are blocking the eruption of the all-important eyeteeth. The oral surgeon will also need to remove any extra teeth (supernumerary teeth) or growths that are blocking eruption of any of the adult teeth. If the eruption path is cleared and the space is opened up by age 11-12, there is a good chance the impacted eyetooth will erupt with nature’s help alone. If the eyetooth is allowed to develop too much (age 13-14), the impacted eyetooth will not erupt by itself even with the space cleared for its eruption. If the patient is too old (over 40), there is a much higher chance the tooth will be fused in position. In these cases the tooth will not budge despite all the efforts of the orthodontist and oral surgeon to erupt it into place. Sadly, the only option at this point is to extract the impacted tooth and consider an alternate treatment to replace it in the dental arch (crown on a dental implant or a fixed bridge).
What Happens If The Eyetooth Will Not Erupt When Proper Space Is Available?
In cases where the eyeteeth will not erupt spontaneously, the orthodontist and oral surgeon work together to get these unerupted eyeteeth to erupt. Each case must be evaluated on an individual basis but treatment will usually involve a combined effort between the orthodontist and the oral surgeon. The most common scenario will call for the orthodontist to place braces on the teeth (at least the upper arch). A space will be opened to provide room for the impacted tooth to be moved into its proper position in the dental arch. If the baby eyetooth has not fallen out already, it is usually left in place until the space for the adult eyetooth is ready. Once the space is ready, the orthodontist will refer the patient to the oral surgeon to have the impacted eyetooth exposed and bracketed.
In a simple surgical procedure performed in the surgeon’s office, the gum on top of the impacted tooth will be lifted up to expose the hidden tooth underneath. If there is a baby tooth present, it will be removed at the same time. Once the tooth is exposed, the oral surgeon will bond an orthodontic bracket to the exposed tooth. The bracket will have a miniature gold chain attached to it. The oral surgeon will guide the chain back to the orthodontic arch wire where it will be temporarily attached. Sometimes the surgeon will leave the exposed impacted tooth completely uncovered by suturing the gum up high above the tooth or making a window in the gum covering the tooth (on selected cases located on the roof of the mouth). Most of the time, the gum will be returned to its original location and sutured back with only the chain remaining visible as it exits a small hole in the gum.
Shortly after surgery (1-14 days) the patient will return to the orthodontist. A rubber band will be attached to the chain to put a light eruptive pulling force on the impacted tooth. This will begin the process of moving the tooth into its proper place in the dental arch. This is a carefully controlled, slow process that may take up to a full year to complete. Remember, the goal is to erupt the impacted tooth and not to extract it! Once the tooth is moved into the arch in its final position, the gum around it will be evaluated to make sure it is sufficiently strong and healthy to last for a lifetime of chewing and tooth brushing. In some circumstances, especially those where the tooth had to be moved a long distance, there may be some minor “gum surgery” required to add bulk to the gum tissue over the relocated tooth so it remains healthy during normal function. Your dentist or orthodontist will explain this situation to you if it applies to your specific situation.
<<<<<<<<INSERT THE ANIMATION SEQUENCE HERE>>>>>>>>
These basic principals can be adapted to apply to any impacted tooth in the mouth. It is not that uncommon for both of the maxillary cuspids to be impacted. In these cases, the space in the dental arch form will be prepared on both sides at once. When the orthodontist is ready, the surgeon will expose and bracket both teeth in the same visit so the patient only has to heal from surgery once. Because the anterior teeth (incisors and cuspids) and the bicuspid teeth are small and have single roots, they are easier to erupt if they get impacted than the posterior molar teeth. The molar teeth are much bigger teeth and have multiple roots making them more difficult to move. The orthodontic maneuvers needed to manipulate an impacted molar tooth can be more complicated because of their location in the back of the dental arch.
Recent studies have revealed that with early identification of impacted eyeteeth (or any other impacted tooth other than wisdom teeth), treatment should be initiated at a younger age. Once the general dentist or hygienist identifies a potential eruption problem, the patient should be referred to the orthodontist for early evaluation. In some cases the patient will be sent to the oral surgeon before braces are even applied to the teeth. As mentioned earlier, the surgeon will be asked to remove over-retained baby teeth and/or selected adult teeth. He will also remove any extra teeth or growths that are blocking eruption of the developing adult teeth. Finally, he may be asked to simply expose an impacted eyetooth without attaching a bracket and chain to it. In reality, this is an easier surgical procedure to perform than having to expose and bracket the impacted tooth. This will encourage some eruption to occur before the tooth becomes totally impacted (stuck). By the time the patient is at the proper age for the orthodontist to apply braces to the dental arch, the eyetooth will have erupted enough that the orthodontist can bond a bracket to it and move it into place without needing to force its eruption. In the long run, this saves time for the patient and means less time in braces (always a plus for any patient!).
What To Expect From Surgery To Expose & Bracket An Impacted Tooth?
The surgery to expose and bracket an impacted tooth is a very straightforward surgical procedure that is performed in the oral surgeon’s office. For most patients, it is performed with using laughing gas and local anesthesia. In selected cases it will be performed under IV sedation if the patient desires to be asleep, but this is generally not necessary for this procedure. The procedure is generally scheduled for 75 minutes if one tooth is being exposed and bracketed and 105 minutes if both sides require treatment. If the procedure only requires exposing the tooth with no bracketing, the time required will be shortened by about one half. These issues will be discussed in detail at your preoperative consultation with your doctor. You can also refer to Preoperative Instructions under Surgical Instructions on this website for a review of any details.
You can expect a limited amount of bleeding from the surgical sites after surgery. Although there will be some discomfort after surgery at the surgical sites, most patients find Tylenol or Advil to be more than adequate to manage any pain they may have. Within two to three days after surgery there is usually little need for any medication at all. There may be some swelling from holding the lip up to visualize the surgical site; it can be minimized by applying ice packs to the lip for the afternoon after surgery. Bruising is not a common finding at all after these cases. A soft, bland diet is recommended at first, but you may resume your normal diet as soon as you feel comfortable chewing. It is advised that you avoid sharp food items like crackers and chips as they will irritate the surgical site if they jab the wound during initial healing. Your doctor will see you seven to ten days after surgery to evaluate the healing process and make sure you are maintaining good oral hygiene. You should plan to see your orthodontist within 1-14 days to activate the eruption process by applying the proper rubber band to the chain on your tooth. As always your doctor is available at the office or can be beeped after hours if any problems should arise after surgery. Simply call Dr. Mills at 925-443-4211 if you have any questions.
go to top >>Oral Pathology
The inside of the mouth is normally lined with a special type of skin (mucosa) that is smooth and coral pink in color. Any alteration in this appearance could be a warning sign for a pathological process. The most serious of these is oral cancer. The following can be signs at the beginning of a pathologic process or cancerous growth:
- Reddish patches (erythroplasia) or whitish patches (leukoplakia) in the mouth.
- A sore that fails to heal and bleeds easily.
- A lump or thickening on the skin lining the inside of the mouth.
- Chronic sore throat or hoarseness.
- Difficulty in chewing or swallowing.
These changes can be detected on the lips, cheeks, palate, and gum tissue around the teeth, tongue, face and/or neck. Pain does not always occur with pathology, and curiously, is not often associated with oral cancer. However, any patient with facial and/or oral pain without an obvious cause or reason may also be at risk for oral cancer.
We would recommend performing an oral cancer self-examination monthly and remember that your mouth is one of your body's most important warning systems. Do not ignore suspicious lumps or sores. Please contact us so we may help.
go to top >>TMJ Disorders
 TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders are a family of problems related to your complex jaw joint. If you have had symptoms like pain or a "clicking" sound, you'll be glad to know that these problems are more easily diagnosed and treated than they were in the past. These symptoms occur when the joints of the jaw and the chewing muscles (muscles of mastication) do not work together correctly. TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint, which is the name for each joint (right and left) that connects your jaw to your skull. Since some types of TMJ problems can lead to more serious conditions, early detection and treatment are important.
TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders are a family of problems related to your complex jaw joint. If you have had symptoms like pain or a "clicking" sound, you'll be glad to know that these problems are more easily diagnosed and treated than they were in the past. These symptoms occur when the joints of the jaw and the chewing muscles (muscles of mastication) do not work together correctly. TMJ stands for temporomandibular joint, which is the name for each joint (right and left) that connects your jaw to your skull. Since some types of TMJ problems can lead to more serious conditions, early detection and treatment are important.
No one treatment can resolve TMJ disorders completely and treatment takes time to become effective. Dr. Mills can help you have a healthier and more comfortable jaw.
Trouble With Your Jaw?
TMJ disorders develop for many reasons. You might clench or grind your teeth, tightening your jaw muscles and stressing your TM joint. You may have a damaged jaw joint due to injury or disease. Injuries and arthritis can damage the joint directly or stretch or tear the muscle ligaments. As a result, the disk, which is made of cartilage and functions as the “cushion” of the jaw joint, can slip out of position. Whatever the cause, the results may include a misaligned bite, pain, clicking, or grating noise when you open your mouth or trouble opening your mouth wide.
Do You Have A TMJ Disorder?
- Are you aware of grinding or clenching your teeth?
- Do you wake up with sore, stiff muscles around your jaws?
- Do you have frequent headaches or neck aches?
- Does the pain get worse when you clench your teeth?
- Does stress make your clenching and pain worse?
- Does your jaw click, pop, grate, catch, or lock when you open your mouth?
- Is it difficult or painful to open your mouth, eat, or yawn?
- Have you ever injured your neck, head, or jaws?
- Have you had problems (such as arthritis) with other joints?
- Do you have teeth that no longer touch when you bite?
- Do your teeth meet differently from time to time?
- Is it hard to use your front teeth to bite or tear food?
- Are your teeth sensitive, loose, broken or worn?
The more times you answered "yes", the more likely it is that you have a TMJ disorder. Understanding TMJ disorders will also help you understand how they are treated.
Treatment
There are various treatment options that Dr. Mills can utilize to improve the harmony and function of your jaw. Once an evaluation confirms a diagnosis of TMJ disorder, Dr. Mills will determine the proper course of treatment. It is important to note that treatment always works best with a team approach of self-care joined with professional care.
The initial goals are to relieve the muscle spasm and joint pain. This is usually accomplished with a pain reliever, anti-inflammatory, or muscle relaxant. Steroids can be injected directly into the joints to reduce pain and inflammation. Self-care treatments can often be effective as well and include:
- Resting your jaw
- Keeping your teeth apart when you are not swallowing or eating
- Eating soft foods
- Applying ice and heat
- Exercising your jaw
- Practicing good posture
Stress management techniques such as biofeedback or physical therapy may also be recommended, as well as a temporary, clear plastic appliance known as a splint. A splint (or nightguard) fits over your top or bottom teeth and helps keep your teeth apart, thereby relaxing the muscles and reducing pain. There are different types of appliances used for different purposes. A nightguard helps you stop clenching or grinding your teeth and reduces muscle tension at night and helps to protect the cartilage and joint surfaces. An anterior positioning appliance moves your jaw forward, relives pressure on parts of your jaw and aids in disk repositioning. It may be worn 24 hours/day to help your jaw heal. An orthotic stabilization appliance is worn 24 hours/day or just at night to move your jaw into proper position. Appliances also help to protect from tooth wear.
What About Bite Correction Or Surgery?
If your TMJ disorder has caused problems with how your teeth fit together, you may need treatment such as bite adjustment (equilibration), orthodontics with or without jaw reconstruction, or restorative dental work. Surgical options such as arthroscopy and open joint repair restructuring are sometimes needed, but are reserved for severe cases. Dr. Mills does not consider TMJ surgery unless the jaw can’t open, is dislocated and nonreducible, has severe degeneration, or the patient has undergone appliance treatment unsuccessfully.
go to top >>Sleep Apnea
People with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) have disrupted sleep and low blood oxygen levels. When obstructive sleep apnea occurs, the tongue is sucked against the back of the throat. This blocks the upper airway and airflow stops. When the oxygen level in the brain becomes low enough, the sleeper partially awakens, the obstruction in the throat clears, and the flow of air starts again, usually with a loud gasp.
Repeated cycles of decreased oxygenation lead to very serious cardiovascular problems. Additionally, these individuals suffer from excessive daytime sleepiness, depression, and loss of concentration.
Some patients have obstructions that are less severe called Upper Airway Resistance Syndrome (UARS). In either case, the individuals suffer many of the same symptoms.
The first step in treatment resides in recognition of the symptoms and seeking appropriate consultation. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons offer consultation and treatment options.
In addition to a detailed history, the doctors will assess the anatomic relationships in the maxillofacial region. With cephalometic (skull x-ray) analysis, the doctors can ascertain the level of obstruction. Sometimes a naso-pharyngeal exam is done with a flexible fiber-optic camera. To confirm the amount of cardiovascular compromise and decreased oxygenation levels, a sleep study may be recommended to monitor an individual overnight.
There are several treatment options available. An initial treatment may consist of using a nasal CPAP machine that delivers pressurized oxygen through a nasal mask to limit obstruction at night. One of the surgical options is an uvulo-palato-pharyngo-plasty (UPPP), which is performed in the back of the soft palate and throat. A similar procedure is sometimes done with the assistance of a laser and is called a laser assisted uvulo-palato-plasty (LAUPP). In other cases, a radio-frequency probe is utilized to tighten the soft palate. These procedures usually performed under light IV sedation in the office.
In more complex cases, the bones of the upper and lower jaw may be repositioned to increase the size of the airway (orthognathic surgery). This procedure is done in the hospital under general anesthesia and requires a one to two day overnight stay in the hospital.
go to top >>